Want to make your home safer and smarter? Start with the right IoT sensors. These devices can protect your family by detecting leaks, fires, and unusual activity while automating everyday tasks like lighting and temperature control. But with so many options, it’s easy to overspend or pick the wrong ones. Here’s a quick guide to help you:
- Identify key areas: Use contact sensors for doors/windows, water sensors near pipes/appliances, smoke/CO detectors in hallways/kitchen, and motion sensors for lighting/security.
- Check signal coverage: Test Wi-Fi or Bluetooth strength in your home, and consider range extenders or Zigbee/Z-Wave for larger spaces.
- Set a budget: Quality safety sensors cost $115–$140, but multipurpose models can save money.
- Ensure compatibility: Match sensors to your smart home system (e.g., Matter, Zigbee, Alexa).
- Prioritize security: Change default passwords, enable encryption, and update firmware regularly.
Get Started with Smart Home Sensors (Beginner’s Guide)
Planning Your Home Monitoring Needs
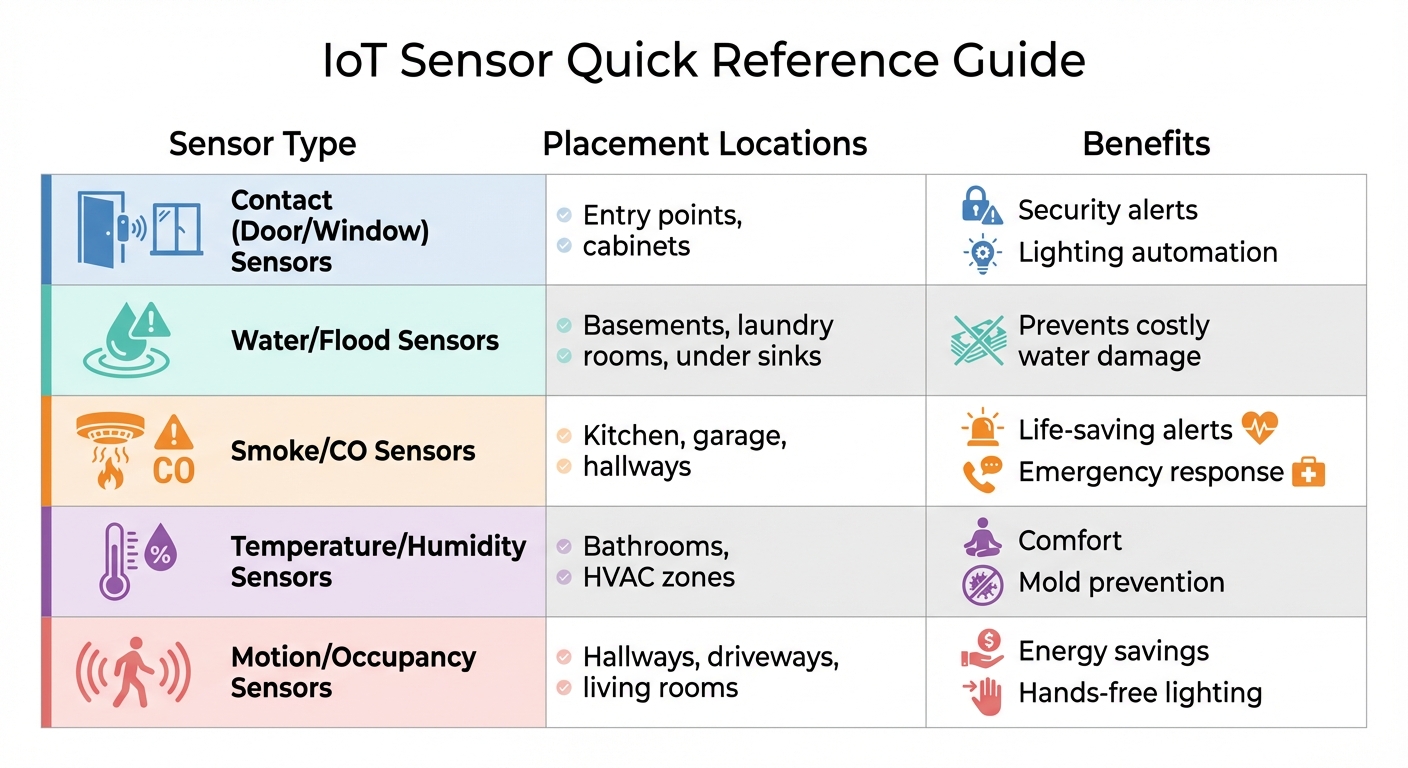
IoT Sensor Types, Placement Locations, and Benefits for Home Monitoring
Identify Which Areas Need Monitoring
Take a walk through your home and pinpoint the spots that need attention. Entry points like doors and windows are ideal for contact sensors, which can alert you if they’re opened unexpectedly. For rooms with multiple windows, a single glass break sensor can cover areas up to 25 feet, offering broad protection.
Water damage is another big concern. Place moisture sensors in areas prone to leaks, such as the basement, under sinks, near the washing machine, or by the dishwasher. For fire safety, smoke and carbon monoxide detectors are essential in places like the kitchen, garage, and hallways.
Don’t forget about everyday comfort. Bathrooms can benefit from humidity sensors that trigger exhaust fans to help prevent mold. In hallways or on stairs, motion sensors can activate path lighting, making nighttime navigation safer. Outdoors, motion sensors can light up driveways or porches and send alerts when visitors arrive.
| Sensor Type | Placement Locations | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Contact (Door/Window) | Entry points, cabinets | Security alerts and lighting automation |
| Water/Flood | Basements, laundry rooms, under sinks | Prevents costly water damage |
| Smoke/CO | Kitchen, garage, hallways | Life-saving alerts and emergency response |
| Temperature/Humidity | Bathrooms, HVAC zones | Comfort and mold prevention |
| Motion/Occupancy | Hallways, driveways, living rooms | Energy savings and hands-free lighting |
Once you’ve identified where sensors are needed, it’s time to evaluate your home’s layout to ensure everything works seamlessly.
Check Your Home Layout and Signal Coverage
Before buying sensors, test your home’s wireless signal strength. WiFi sensors generally work within 164 feet of a router, while Bluetooth sensors need to stay within about 20 feet of a hub. Walk around your home with your phone to check the WiFi signal in the areas where you plan to install sensors. If the signal is weak, you might need a range extender.
Be mindful of obstacles like thick walls, metal furniture, or large appliances, as these can block wireless signals. High-voltage power lines and other electronic devices may also interfere with connectivity or affect sensor accuracy. For environmental sensors like air quality monitors, placing them 3 to 6 feet above the floor – within the "breathing zone" – provides the most accurate readings.
Motion sensors perform best when someone moves across their field of vision rather than directly toward them. Test the placement using the sensor’s app before mounting it permanently to avoid dead zones. If you’re monitoring a detached garage or outbuilding, Zigbee or Z-Wave sensors with range extenders might be more reliable than WiFi.
Understanding your home’s signal coverage will help you choose the right sensors and features within your budget.
Set Your Budget and Choose Must-Have Features
Safety should always come first. High-quality safety sensors typically cost between $115 and $140. Considering that fires, water damage, and theft account for 97.3% of all insurance claims, investing in these devices could save you from costly repairs down the line.
Look for multipurpose sensors that combine features like motion, temperature, and light detection to get the most value for your money. Also, ensure the sensors are compatible with your smart home system – whether it’s Apple HomeKit, Amazon Alexa, Zigbee, or Z-Wave.
Don’t overlook ongoing expenses. Most sensors run on batteries that last 1 to 3 years. Check if there are any additional costs, such as monthly monitoring or cloud storage fees. Lastly, confirm that the sensors can function locally without internet access. This ensures that critical alerts won’t be missed during power outages.
What to Look for When Choosing IoT Sensors
Check Compatibility with Your Smart Home System
Once you’ve identified your monitoring needs, the next step is to ensure the sensors you choose will work seamlessly with your existing smart home setup.
Start by checking the communication protocols your smart home hub supports. These might include Zigbee, Z-Wave, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Thread, or Matter. Each protocol has its strengths, but Matter stands out as a newer standard designed to make devices from brands like Apple, Google, and Amazon work together without compatibility issues. If you’re starting from scratch, opting for Matter-compatible sensors can save you headaches later. Additionally, Thread, a low-power mesh protocol often used with Matter, allows devices to communicate without needing a central bridge.
Some sensors may require a proprietary hub, such as those from Philips Hue or Ring, while others can connect directly to universal hubs like Samsung SmartThings or certain Amazon Echo models with built-in Zigbee or Matter support. To avoid frustration, check your smart home controller’s official compatibility list before buying.
Interestingly, a single motion sensor can often handle multiple tasks. For example, it could turn on lights, adjust the thermostat, and even serve as a security alert all at once.
Verify Accuracy, Reliability, and Battery Life
The performance of a sensor is critical for long-term reliability, so it’s worth digging into details like accuracy and battery life.
Look for sensors with strong battery performance. High-quality models can last between 2 and 8 years, thanks to features like adaptive sampling, which balances how often the sensor checks conditions with power efficiency. Sensors using low-power protocols like Zigbee, Z-Wave, or Sub-GHz frequencies typically offer better battery life and range compared to Wi-Fi-based sensors, which tend to consume more energy.
For accurate and stable readings, pay attention to the sensor’s drift rating. Top-tier sensors can detect even slight changes, such as humidity shifts as small as 0.1%. Modular designs are another smart choice – they let you replace just the sensing component instead of the entire unit when recalibration is necessary. If you have pets, consider motion sensors with pet immunity features that ignore movements from animals weighing up to 55 lbs, reducing false alarms.
Finally, don’t overlook your gateway’s capacity. High-quality gateways can support over 50 devices across multiple floors, while more basic models might only handle around 10.
Consider Size, Design, and Installation Options
Compact and well-designed sensors can blend seamlessly into your home, and multipurpose units that combine motion, temperature, and light detection can help you minimize the number of devices needed in each room.
When it comes to installation, flexibility is key. Look for sensors with various mounting options, such as adhesive, magnetic, or recessed mounts, to suit your space. Battery-powered models are especially convenient, as they eliminate the need for wiring. For unique setups, like non-standard door or window frames, use specialized mounting accessories to ensure proper alignment. If you prefer a discreet look, recessed contact sensors are an option, though they do require some drilling.
Placement also matters. Mounting motion sensors high on walls can maximize their coverage area while reducing false triggers from pets or low-level activity. Some models offer a 110-degree viewing angle and can detect movement up to 20 feet away.
For areas prone to moisture or dust, such as bathrooms, basements, or outdoor spaces, check the sensor’s IP (Ingress Protection) rating to ensure durability. Water sensors come in two main types: point sensors, which detect leaks in specific spots like under a pipe, and cable sensors, which monitor larger areas, such as along basement walls.
Make sure the sensors you choose align with your home’s layout and design preferences while meeting your functional needs.
Installing and Connecting Your Sensors
Where to Place Sensors for Best Results
Once you’ve chosen your sensors and planned their placement, it’s time to install them effectively. Proper positioning is key to ensuring your sensors work as intended. As Derek Prall, a Home Security Expert at SafeHome.org, explains:
Security sensors are only as good as their placement.
Motion sensors should be mounted 6–8 feet high on a wall or in a corner to provide a broad view of the room. Avoid placing them near heat sources like radiators, vents, or space heaters, as these can trigger false alarms. Similarly, keep them out of direct sunlight – infrared radiation from sunlight can confuse PIR sensors. If you have large pets, avoid installing motion sensors at the top of stairs; as your pet climbs, it may appear larger to the sensor and trigger a false alarm.
Contact sensors require precise alignment, with their two components no more than 0.5 inches apart to maintain the magnetic field. Avoid mounting them on metal surfaces, such as steel doors, as metal can disrupt both the magnetic field and the radio signals. Air quality sensors should be positioned 3–6 feet above the ground in areas with good airflow. Keep them away from grills or dense vegetation, which could affect their accuracy. Leak detectors should be placed directly on the floor in areas prone to water leaks, such as under sinks, near water heaters, or behind washing machines and dishwashers.
Keep in mind that materials like concrete, brick, and plaster can weaken radio signals. Minimizing the number of walls between your sensors and the hub will help maintain strong communication.
Set Up and Test Each Sensor
Proper installation is essential for reliable home protection, so take the time to set up and test each sensor carefully.
Start by connecting your hub to the internet and registering it to your user account. Many manufacturers recommend registering each sensor in the management app before inserting the batteries.
Once the sensors are powered on, check their LED indicators. A double green flash usually means the sensor is working correctly, while a red flash indicates a problem. During the initial setup, some sensors transmit data every 30 seconds to make verification easier.
Use the companion app to confirm that the sensors are reporting data. Manually test each sensor to ensure they’re functioning: open and close doors for contact sensors, walk in front of motion detectors, or place a damp cloth on leak detectors. If you’re testing a leak detector with an alarm, you’ll hear it immediately when moisture is detected.
Check the signal strength (RSSI) in your app. Weak signals can lead to intermittent reporting, even if the initial test seems fine. Take photos of your sensor installations for future reference. Keep an eye out for unusual data spikes – these could indicate power supply issues or interference from nearby appliances like air conditioners.
sbb-itb-6893d99
Protecting Your Family’s Privacy and Data
Your home monitoring sensors gather sensitive details about your family’s daily routines. With IoT devices facing an average of 5,200 attacks every month and the percentage of companies reporting breaches from IoT devices jumping to 53% in 2024 (up from 30% in 2018), securing this data is more important than ever.
Now that your sensors are up and running, taking steps to protect the information they collect is essential for your family’s safety.
Change Default Passwords Immediately
Most manufacturers use the same default usernames and passwords across their devices, and these credentials are often easy to find online. Julie Haney, a Cybersecurity Researcher at NIST, emphasizes:
Do not reuse your passwords! Many attacks on smart home devices, including incidents where hackers accessed video monitors to talk to babies, have been traced back to reused passwords.
Create unique passwords for every device, using at least eight characters with a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. Don’t forget to change your router’s default administrative password as well – your router acts as the "front door" to your smart home. If it’s compromised, every connected sensor could be at risk.
Turn On Encryption and Keep Firmware Updated
Strong passwords are just the first step. Ensuring your data is secure while it’s being transmitted is equally important. Set your router’s wireless security to WPA3 (or WPA2 if WPA3 isn’t available) to encrypt data traveling between your sensors and the internet. Check your devices’ apps or administrative settings for options like "Encryption" or "Secure Transfer", and enable them. Also, disable any Peer-to-Peer (P2P) features, as these can create weak spots that hackers can exploit.
Regular firmware updates are critical, too, as they fix security vulnerabilities. Turn on automatic updates whenever possible, or make it a habit to check for updates at least once every three months.
Set Up Access Controls and Two-Factor Authentication
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) or Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of protection to your device accounts. This typically involves entering a code sent to your phone, making it much harder for anyone to break in, even if your password is stolen. Julie Haney explains:
Multi-factor authentication… will help protect you if your password or PIN is exposed.
Another smart move is to create a guest Wi-Fi network specifically for your IoT devices. This separates your sensors from computers and phones that hold sensitive financial or personal data. Additionally, keep an eye on your router’s access logs to spot and disconnect any unknown or suspicious devices attempting to connect.
| Security Layer | Action Item | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Router | Enable Guest Network | Keeps IoT sensors separate from sensitive devices. |
| Device Account | Enable 2FA/MFA | Adds an extra verification step for better security. |
| Device Hardware | Disable P2P/Remote Access | Eliminates vulnerable external access points. |
| Software | Install Firmware Patches | Fixes known bugs and security flaws. |
Keeping Your Sensors Running Smoothly
Taking care of your sensors through regular maintenance is key to keeping them reliable and performing well over time. A little effort now can prevent failures and ensure your home stays protected without interruptions.
Check and Replace Batteries on Schedule
Different sensors draw power at different rates, so it’s important to adjust your battery checks accordingly. Devices like smart locks and wireless cameras, which tend to use more power, should have their battery levels reviewed weekly using your smart home app. This helps avoid issues like lockouts or losing video feeds. On the other hand, smoke detectors and medical alert devices usually only need a monthly test, which you can do by pressing their test buttons.
Alina Bradford, a Safety and Security Expert at SafeWise, recommends:
It’s best to take a look at the app to see how your devices are doing each week.
Additionally, every six months, test your sensors by triggering them to ensure they’re functioning properly. Check that they’re securely mounted, as humidity or everyday household activity can sometimes loosen their attachments. Some advanced sensors, like the Kaiterra Sensedge Go, boast battery lives of up to 8 years thanks to adaptive sampling technology. Others, such as Tapo‘s sub-G frequency sensors, typically last around 2 years before needing a battery replacement.
Install Updates and Check Sensor Performance
Firmware updates are more than just bug fixes – they’re crucial for patching security vulnerabilities and enhancing sensor accuracy. Whenever possible, enable automatic updates in your smart home app or hub settings to ensure your devices stay protected. If automatic updates aren’t an option, make it a habit to check your monitoring system monthly for any available updates.
Keeping firmware up to date also improves reliability. In fact, businesses that prioritize consistent software management can reduce machine downtime by 50% and cut maintenance costs by up to 40%.
Beyond software, it’s important to monitor sensor performance. For instance, air quality monitors may collect dust over time, which can affect their accuracy. Some models require periodic calibration or sensor replacements to maintain reliable readings. If you notice inconsistent data or delayed alerts, check the sensor’s placement and signal strength before assuming it’s a hardware problem. This proactive care ensures your sensors stay both accurate and secure.
Review Security Settings Regularly
Your security settings can change unexpectedly – sometimes due to firmware updates resetting configurations or new vulnerabilities being discovered. Set a reminder to review your security setup every three to six months.
Start by logging into your router’s web interface to review connected devices. Look for any unfamiliar or “ghost” devices that might indicate unauthorized access. For high-risk devices like cameras, it’s a good idea to check administrative access logs for unusual IP addresses or login attempts. Make sure encryption is enabled, two-factor authentication is active, and any unused remote management features are turned off.
After conducting your review, disable any features or sharing options you no longer need. Each unnecessary feature left active could serve as a potential entry point for attackers. Regularly fine-tuning your security settings helps keep your system safe and ensures peace of mind.
Conclusion
This checklist simplifies the process of selecting and setting up IoT sensors for your home. Start by identifying what matters most – prioritize essential safety devices like smoke detectors, carbon monoxide monitors, and water leak sensors before considering convenience features like climate control or lighting automation. This approach ensures you address critical safety needs first, creating a strong foundation for a smarter, safer home.
Placing sensors strategically and setting them up correctly reduces false alarms and guarantees comprehensive coverage. By following a thoughtful plan for installation and maintenance, you can achieve both safety and efficiency.
The key is proactive management. As one housing provider wisely put it:
It’s better to work on a problem, rather than a crisis.
Taking action now prevents costly surprises later. With over 15 billion IoT devices already in use worldwide, this technology has shown its value in catching problems early – like detecting a slow water leak that could otherwise lead to an average of $6,965 in damages.
For busy parents, this approach offers more than just security – it provides peace of mind. Your sensors take care of routine monitoring, only alerting you when something requires attention. Once installed and functioning properly, upkeep becomes as simple as a quarterly check, freeing you from daily worries.
Start with the essentials, and expand your system as needed. A little planning upfront saves time, money, and stress while helping you create a safer and more efficient home.
FAQs
How can I make sure my IoT sensors work with my smart home system?
To make sure your IoT sensors work seamlessly with your smart home setup, start by verifying their communication protocols. Most smart home systems rely on Z-Wave, Zigbee, or Wi-Fi, so it’s crucial to confirm which protocol your hub supports. Once you know, pick sensors that align with it. If your hub supports multiple protocols, you can combine devices with ease, as the hub will manage the integration for you.
Next, check the compatibility details provided by the manufacturer or refer to your hub’s guide for supported devices. Look for labels like “works with Amazon Alexa, Google Home, or Apple HomeKit.” Steer clear of stand-alone sensors that only function through their own app, as they can complicate automation. Instead, choose sensors that integrate directly with your hub for smoother operation and control.
Lastly, pay attention to practical considerations like Wi-Fi band compatibility (most devices stick to 2.4 GHz), power options (battery-powered or wired), and keeping firmware updated. Testing the sensor through your hub’s app before fully committing can save you from headaches and ensure everything runs smoothly in your system.
What are the best affordable IoT sensors for improving home safety?
For keeping your home safe, motion sensors, smoke and carbon monoxide detectors, and water leak sensors are some of the most budget-friendly and effective IoT tools you can invest in. Take motion sensors, for instance – the Samsung SmartThings Motion Sensor, priced at about $39.99, is a solid option for detecting movement and boosting home security.
Smart smoke and carbon monoxide detectors, which usually cost less than $100, offer life-saving alerts to keep your family safe. Meanwhile, water leak sensors, often available for under $50, can alert you to leaks before they cause expensive damage. These devices are not only affordable but also simple to integrate into your smart home setup, making them a practical choice for any household.
What’s the best way to improve Wi-Fi coverage for IoT sensors in a large home?
To boost Wi-Fi coverage for IoT sensors in a large home, start by adjusting your router’s placement. Ideally, place it in a central location, elevated, and away from walls, large furniture, or metal appliances. This setup helps maintain a strong signal, especially for sensors relying on the 2.4 GHz band, which can better penetrate walls.
If certain areas of your home still lack coverage, upgrading to a mesh Wi-Fi system could be the solution. Mesh networks use multiple nodes to create seamless coverage throughout your space. Another option is to use a Wi-Fi extender or add a second access point configured to the same network, extending the signal where needed.
To minimize interference, keep devices like baby monitors, cordless phones, and microwaves away from your sensors. Also, make sure your router’s firmware is updated regularly. These adjustments will help your IoT sensors stay connected, ensuring reliable and hassle-free home monitoring.






